Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a general neurodevelopmental disorder that influences people of all ages. While ADHD is often associated with children, it is estimated that 4.4% of adults in the United States also have it.
This article will explore what ADHD is, the importance of recognizing its symptoms, how it affects adults differently, and the various treatment options available for adults with ADHD.
What is ADHD?
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that changes a person’s ability to pay attention, control impulses, and regulate behavior. It is a chronic condition that can last throughout a person’s life. The three main types of ADHD include inattentive, hyperactive-impulsive, and combined.
- Inattentive type ADHD is characterized by inattention, difficulty paying attention, and forgetfulness.
- Hyperactive-impulsive ADHD is characterized by hyperactivity and impulsivity, such as fidgeting and interrupting others.
- Combined type ADHD involves symptoms of both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
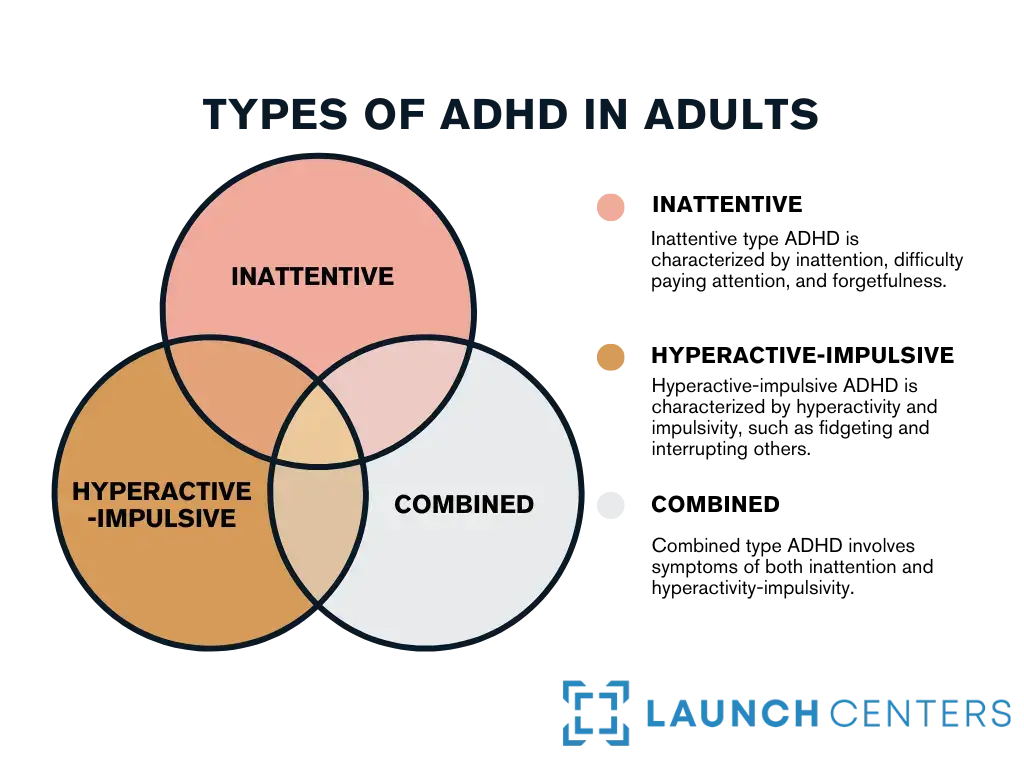
Understanding Adult ADHD
ADHD affects the way the brain processes information and is known to interfere with daily functioning. While the symptoms of ADHD are usually first noticed in childhood, many people do not receive a formal diagnosis until adulthood.
Why Recognizing Symptoms is Important
Recognizing the symptoms of ADHD is important because it can significantly impact a person’s life. Without proper treatment, ADHD can lead to relationship issues, career and work issues, substance abuse, and other mental health concerns. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking treatment, individuals with ADHD can improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of developing additional problems.
ADHD Vs ADD
ADHD stands for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, while ADD stands for Attention Deficit Disorder. In the past, ADD was used to describe individuals who had symptoms of inattention but did not display hyperactivity or impulsivity.
However, in the most recent version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), ADD is no longer a separate diagnosis. Instead, the term ADHD is used to describe individuals who have symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity, or a combination of these.
How ADHD Affects Adults Differently
ADHD can affect adults differently than children. While children with ADHD may struggle with academic performance and social skills, adults with ADHD may struggle with organization, time management, and maintaining relationships. They may also experience low self-esteem, anxiety, and depression.

Causes of ADHD
The correct cause of ADHD is unknown, but it is considered a fusion of genetic and environmental factors. Research has shown that ADHD is hereditary, and certain environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins and maternal smoking during pregnancy, may increase the risk of developing the condition.
Common Symptoms of ADHD
Common symptoms of ADHD in adults include difficulty paying attention, forgetfulness, disorganization, procrastination, impulsivity, and restlessness. Adults with ADHD may also have difficulty following through with tasks, completing work on time, and maintaining relationships.
Recognizing the symptoms of ADHD in adults can be challenging because they may be mistaken for other conditions, such as depression or anxiety. It is essential to look for behavior patterns, such as consistently being late for appointments or forgetting important dates.
Distinguishing between ADHD and other conditions can be difficult because the symptoms may overlap. A healthcare expert can conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms.
Effects of Untreated ADHD in Adults:
- Relationship issues: Unprocessed ADHD can have a significant impact on relationships. Adults with ADHD may have difficulty maintaining friendships and romantic relationships due to forgetfulness, impulsivity, and poor communication skills.
- Career and work issues: ADHD can also affect a person’s career and work performance. Adults with ADHD may have difficulty staying focused on tasks, meeting deadlines, and completing work on time.

Can ADHD Lead To Substance Abuse?
Studies have shown that adults with ADHD are likelier to develop substance abuse and addiction issues than those without the disorder. It may be due to the impulsivity and risk-taking behaviors associated with ADHD.
Untreated ADHD can also increase the risk of developing other mental health concerns like anxiety and depression. These environments can further exacerbate the symptoms of ADHD and make it more challenging to manage.
Diagnosing ADHD in Adults
Diagnosing ADHD in adults involves a comprehensive evaluation of their medical history and symptoms and is usually conducted by a psychiatrist or psychologist in collaboration with other healthcare providers. To determine the underlying cause of the symptoms, various tests and assessments, such as a physical exam, psychological evaluation, and behavioral and cognitive tests, may be used. These assessments not only assist in identifying the underlying cause of the symptoms but also help rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Adult ADHD
- Medications: Medications are a standard treatment option for adults with ADHD. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, are typically prescribed to help improve attention and reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity.
- Therapy: Therapy can also be an effective treatment option for adults with ADHD. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychotherapy can help individuals develop coping strategies and improve their social skills and communication.
- Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as better sleep habits, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet, can also help manage the symptoms of ADHD.
Managing ADHD Symptoms at Home
- Organization and time management strategies: Individuals with ADHD can benefit from developing organization and time management strategies, such as creating a schedule and breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps.
- Stress management techniques: Stress management abilities like meditation and deep breathing exercises can help individuals with ADHD manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
- Exercise and diet: Routine exercise and a healthy diet can also help manage the symptoms of ADHD by improving mood and reducing impulsivity.

Supporting Someone with ADHD:
- Understanding the challenges: It is essential to understand the challenges individuals with ADHD face to provide adequate support. These challenges may include difficulty with organization, time management, and communication.
- Communication strategies: Effective communication is vital when supporting someone with ADHD. Using clear and concise language, active listening, and providing positive reinforcement can help improve communication and strengthen relationships.
- Helping with treatment and management: Supporting someone with ADHD may involve helping them adhere to their treatment plan and develop coping strategies to manage their symptoms.
ADHD Treatment at Launch Centers
If you’re struggling to manage ADHD or know someone who could benefit from treatment, contact Launch Centers in Los Angeles. Our healthcare professionals specialize in creating customized treatment plans to address your unique needs and challenges, which may include medication management, therapy, and lifestyle changes. We closely monitor medication to ensure its effectiveness and minimize side effects.





